Melbourne seawater reverse osmosis desalination plant (Australia)
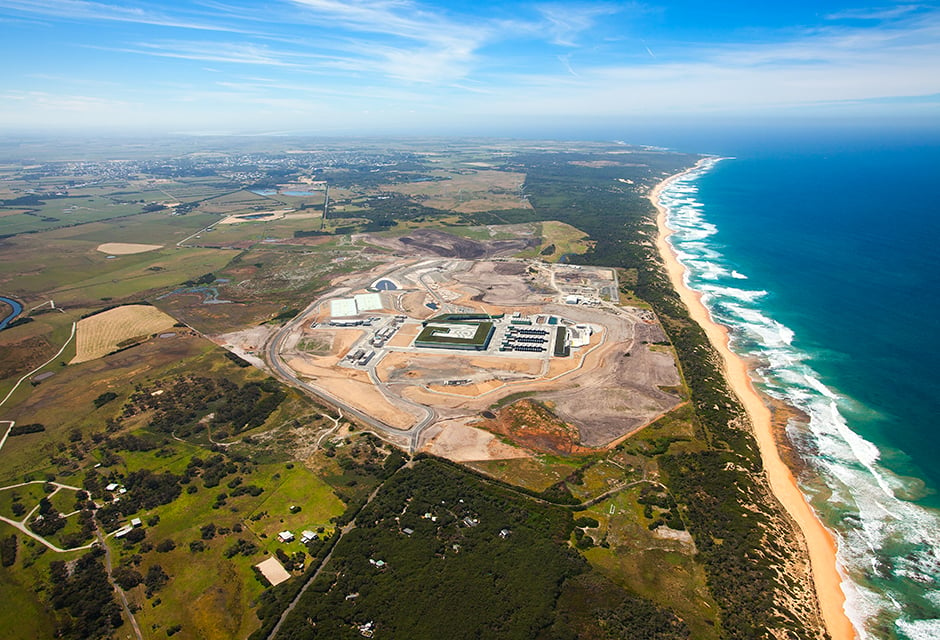

Delivering a safe and reliable desalination water supply to Victoria, Australia.
The Victorian desalination plant, based near Wonthaggi, is able to provide a source of drinking water independent of rainfall and open-air storage for Melbourne and some regional communities. It will be capable of supplying up to 450,000 m3 of drinking water per day.
The AquaSure consortium which brings together Degrémont & Thiess, has been contracted by the Victorian government to finance, design, build, operate and maintain the Victorian Desalination Plant for the 30-year project term.
This AUD 4.8 billion Victorian Desalination Project is a Public Private Partnership (PPP) which has delivered the biggest desalination plant in Australia and one of the biggest in the world.
site visit

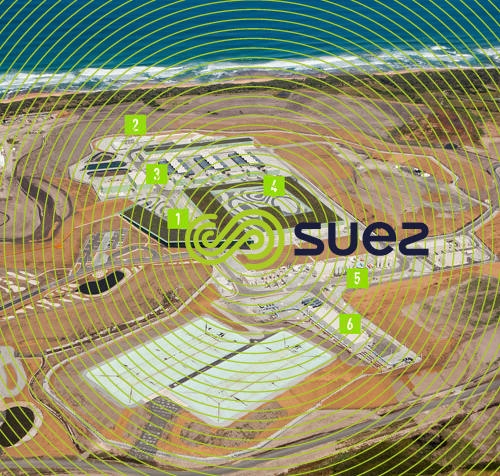

1-Administrative and utilities complex
The administration building accommodates operation and maintenance staff, the operational control centre, which is the heart of the desalination plant, and a research and development laboratory, monitoring quality and process optimisation.
2-Sea water lift pumping station
(SWLPS) transfers seawater from the underground tunnels to the desalination treatment line. It also returns seawater concentrate to the outlet at the end of the process.
- 12 pumps, each capable of moving up to 1m3/second.
3-Pre-treatment
The pre-treatment process is one of the key elements contributing to the performance and to the efficiency of the reverse osmosis facility. This area contains a number of screening facilities to sort both large and fine particles from raw seawater (such as sand and sediment), before it is desalinated.
- 3 large drum screens to sort out seaweed and other large suspended solids.
- 72 Dual Media Pressure Filters (DMPF) to filter smaller particles.
4-Reverse Osmosis building or desalination process
Reverse Osmosis (RO) is a desalination process that uses membrane technology. Filtered seawater passes through two stages of reverse osmosis, where it is pushed through membranes under high pressure to separate salt and water molecules. In the end, pure water is left on one side, and seawater concentrate (brine) on the other.
- A desalination plant of 3 streams, with 51 reverse osmosis racks
- Seawater pushed through 55,000 membranes to separate salt from water
5-Potabilisation line
This is the stage where desalinated water is re-mineralised to meet high quality drinking water standards after the pre-treatment and desalination processes. This area comprises 14 buildings including the lime buildings, RO chemicals, treated water storage, ponds, sludge and solids treatment buildings.
6-Transfer pump station
The water transfer pipeline is able to carry up to 200 million m3 of water annually to Cardinia reservoir.
- The drinking water is stored before it is distributed into the Melbourne and regional water network.
- Water outlet, through which the seawater concentrate, is safely returned to the ocean through diffuser structures.
- Ocean currents dilute the concentrate within seconds.
operation and maintenance till 2039
Members of the O&M team have been involved in the project since the beginning, providing specific input with respect to design, development and construction activities.
- Full asset management including process equipment and civil infrastructure
- Maintenance of the ecological reserve and the transfer pipeline
- More than 50,000 components to maintain
- A team of 50 people
Bookmark tool
Click on the bookmark tool, highlight the last read paragraph to continue your reading later










