minor losses in the pipelines, fittings, valves… for water
Reading time:sudden constriction

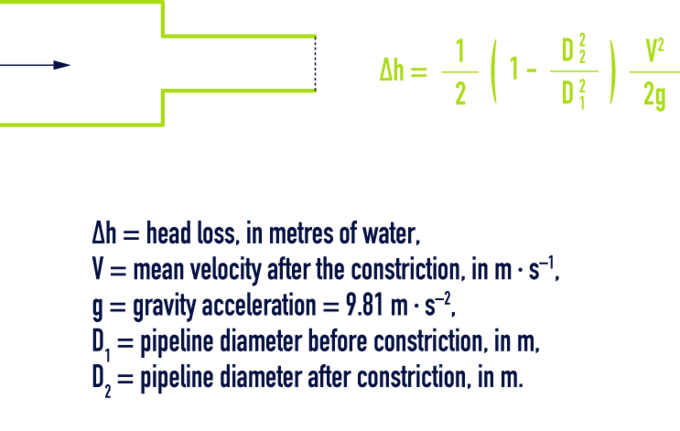
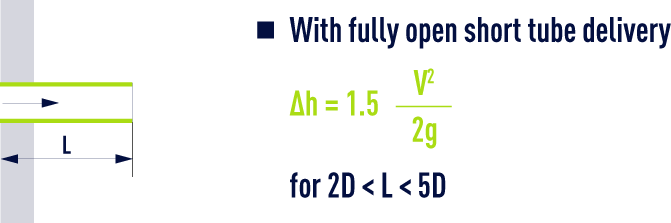
Special case: pipe emerging from a large tank

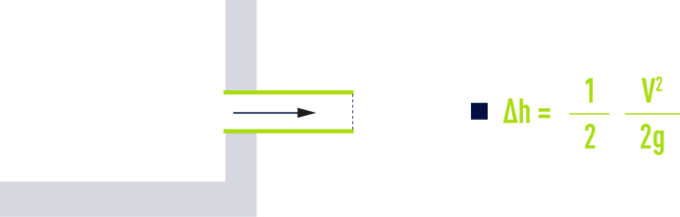



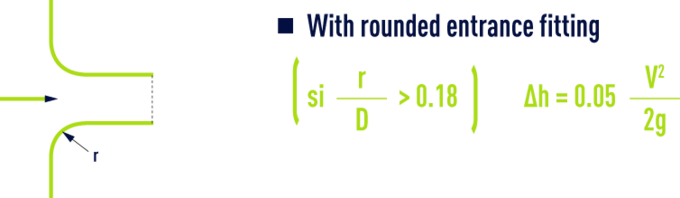

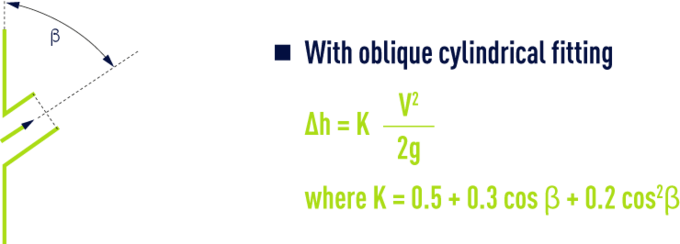




sudden enlargement

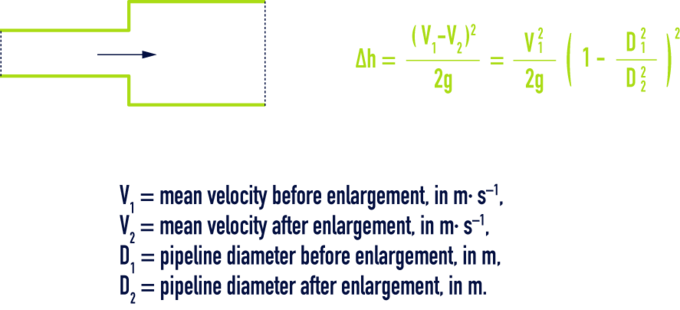
Special case: pipe entering into a large tank


inlet taper

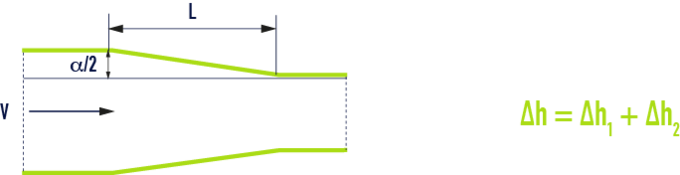
friction loss (∆h1)
Evaluate pressure drop ∆h1', in a cylindrical pipe of the same length and having a section equal to the large section :

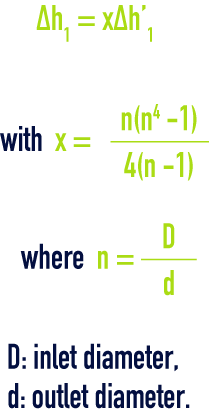
head loss by detachment (∆h2)

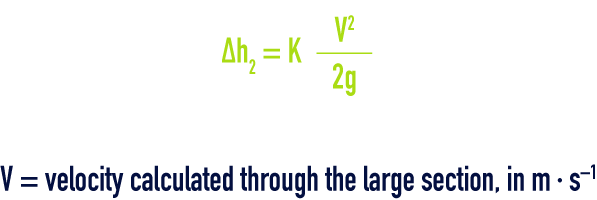
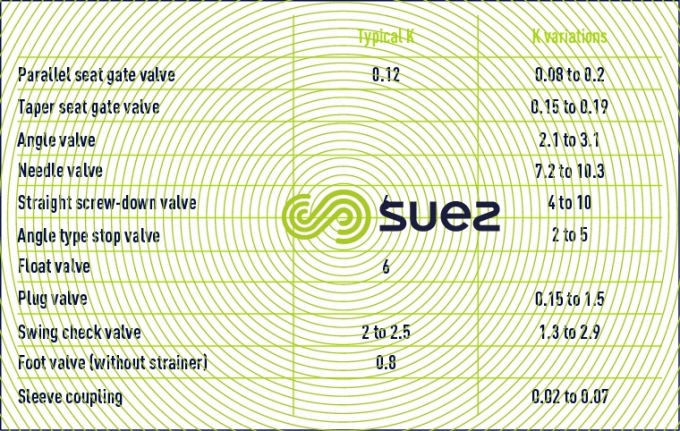
Values for K (table 57) :

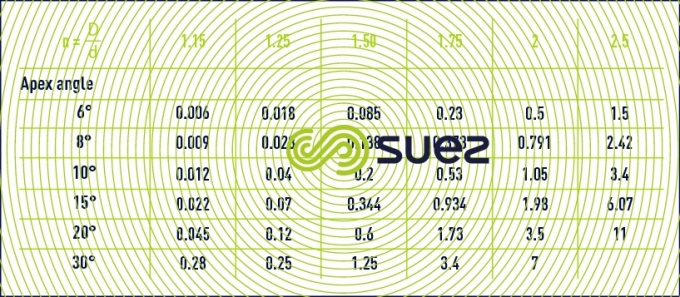

outlet taper
lorenz formula

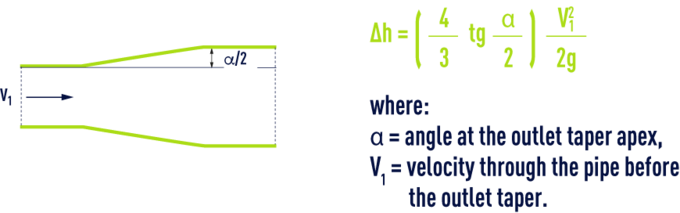
bends
rounded bends

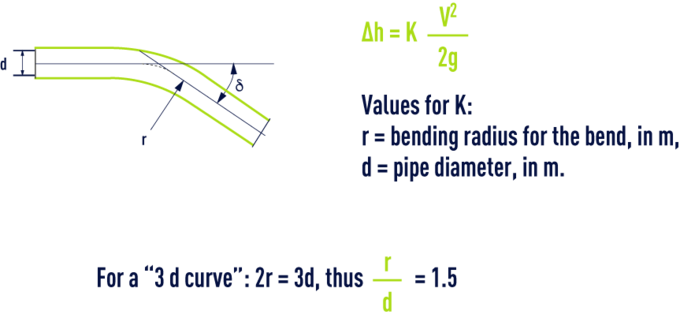



Elbow delivering into a closed tank (K total)






sharp bends :

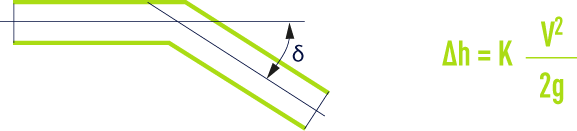



T components
It is assumed as follows :
- branch pipes have the same diameter as the main pipe;
- couplings have sharp angles.
outgoing branch pipe





inlet branch pipe

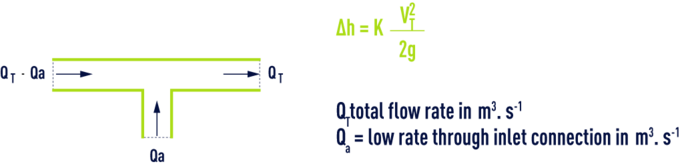



symmetrical T, flow separation: (welded steel T)

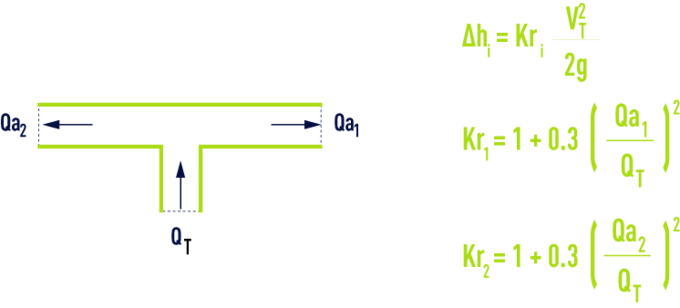
symmetrical T, converging flows

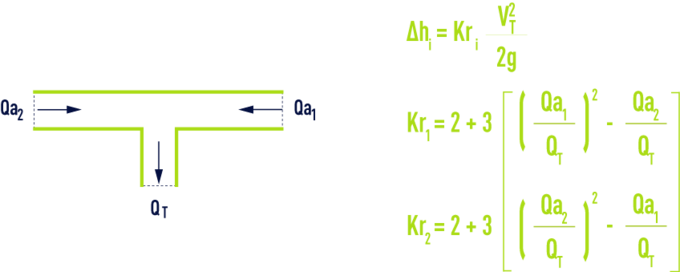
valves and taps

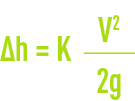
rotating or butterfly valves

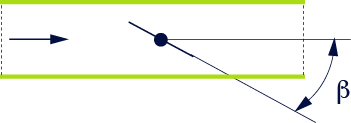
The head loss coefficient according on the valve opening angle depends on the hydraulic profile of the butterfly: for guidance, table 63 provides a few typical values; however, it is advisable to refer to manufacturer tables for greater clarification.



gate valve






plug valve






flap valves






open valves and couplings

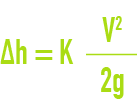


valve coefficient Cv
The normal practice consists in allocating a flow coefficient Cv to the different openings. By definition, Cv is the water flow at 15°C expressed in US gpm that travels through the constricted section for a 1 psi head loss, which is more or less equivalent to the water flow expressed in litres per minute, creating a head loss of 5 mbar or 0.05 m of WC .
Therefore, for water, we have :

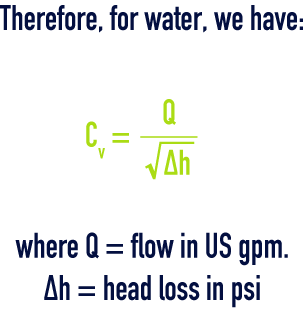

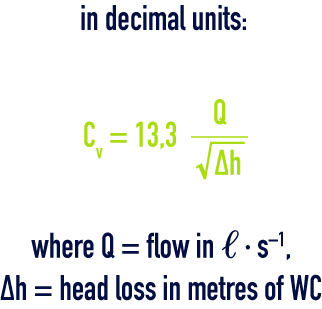
Bookmark tool
Click on the bookmark tool, highlight the last read paragraph to continue your reading later












