lamellar settling tanks
Reading time:lamellar modules
Please refer to lamellar sedimentation for a description of the principle underlying these modules. Depending on the type of water to be treated, the choice of module and its layout has enabled SUEZ to optimise lamellar settling.
selection the module:
- choosing the section: we have opted for a hexagonal section because, in addition to the advantages described in Fundamental physical-chemical engineering processes applicable to water treatment, it produces plaques that hook up easily and that do not give way under the weight of the sludge;
- choosing a diameter (table 1):
- the DH50 has been designed for clarification and carbonate removal;
- the DH80 has been designed for use with UWW, this mesh being large enough to avoid any blockages





layout
Separation effectiveness depends on the quality of equal water distribution in the lamellar modules: a downstream distribution system (degremont®, patent) has been developed that makes it possible to obtain local velocities through the lamellar very close to mean velocities whereas these velocities would routinely be twice as high in the preferential path areas through lamellar settling tanks that are not equipped with an efficient equal distribution system.
Thus, the choice of module and equal distribution will ensure quality clarified water, even at high treatment velocities.
lamellar settling tanks without flocculation : sedipac D and 3D
These units are lamellar settling tanks without reagents and are mainly used in UWW primary settling.
sedipac D
The Sedipac D is a primary lamellar settling tank. Its main function consists in separating out settleable matter from raw water. It is installed downstream from a conventional pre-treatment (barscreening, grit removal, grease removal).
Comment: the Sedipac D can be used as a desludging unit for clarifying water that has highly fluctuating suspended solids concentration levels that can reach several grams per litre; in this case, polymer must be injected via a static mixer upstream from the Sedipac D.
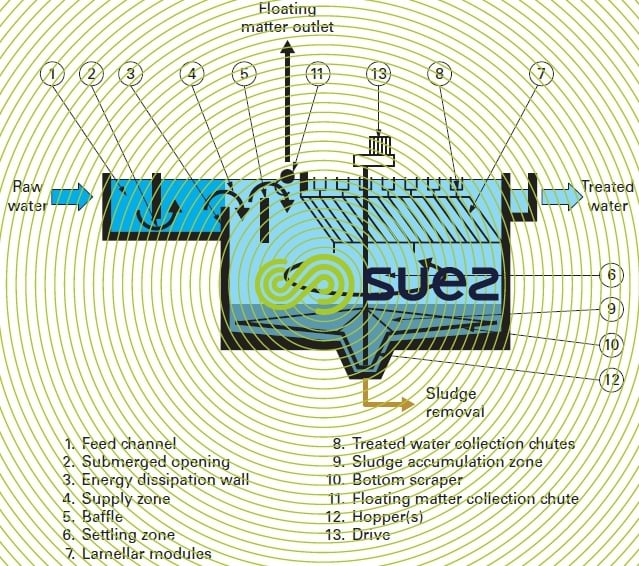
operating principle (figure 9)
Raw water is distributed over the entire width of the Sedipac D from a supply channel (1) through a series of submerged openings (2). It comprises:
- an infeed zone (4);
- a floating matter collection system (11);
- a square section settling area (6);
- lamellar modules (7) for polishing clarification;
- patented, compartmented collection troughs (8);
- a sludge accumulation zone (9) where the scraper (10) and its drive (13) thicken the sludge. The extent of thickening depends on the sludge contact time on the tank floor and, therefore, on the sludge extraction method;
- central or peripheral sludge collection depending on diameter.


advantages
- a tried and tested lamellar settling tank (principle and construction identical to those applicable to the Densadeg, see sludge recirculation settling tank – thickener : the densadeg, or more than 300 in service) that maintains good performances up to velocities of 20 m · h–1 through the lamellar zone thus 12 m · h–1 over the entire settling tank area;
- small overall dimensions; for an identical performance, the Sedipac D is noticeably three times smaller than a conventional non-lamellar settling tank as demonstrated by the following comparison of tank floor hydraulic loading (table 2).



the sedipac 3D
operating principle
The Sedipac 3D has been designed to combine the functions of Grit Removal, Grease removal and Primary settling tank in one single unit. This allows us to reduce the overall surface area covered by primary treatment (structures and their connections) and to regroup within the same area of the plant the output of all by-products (grit, grease, primary sludge) and, consequently, simplify covering and odour control.
This unit eliminates:
- up to 90% of grit > 200 μm;
- up to 15% of SEH (substances extracted using hexane), accounting for 90% of non-emulsified, solidified grease contained in the raw water of a conventional UWW treatment plant (see also great removers);
- up to 75% of suspended solids.
This system does not consist of just three functions housed in the same tank; on the contrary, its strength comes from the fact that it is simultaneously responsible for:
- breaking down each of the functions into elementary stages in order to enhance performance;
- superimposing a proportion of these hydraulically compatible functions in order to achieve greater compactness (approximately 20%) and to simplify operations.
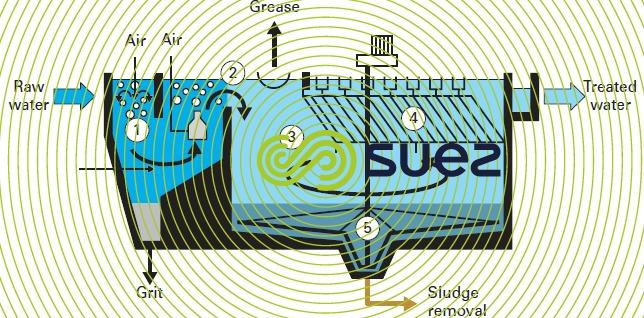
description (figure 10)
- a grit removal zone that includes grit stripping (1), sedimentation and removal of the grit beneath the agitated zones (1+2);
- a grease removal zone that includes a fine bubble production and mixing stage (2) and a stage during which floating matter accumulates before being collected (2+3);
- a lamellar settling zone that includes a stage during which the matter capable of settling is separated through lamellar modules (4) and a stage during which sedimented sludge is removed (4+5). The extent of thickening will depend on the sludge extraction method;
- the grease remover is dovetailed into the upper portion of the grit remover and of the settling tank. Therefore, the grease remover occupies a zero specific surface area. Consequently, the Sedipac 3D’s ground surface coverage is:
- 3 to 4 times smaller than for a conventional solution (grit remover/grease remover and static settling tank);
- approximately 20% less compared with a grit remover/grease remover followed by a Sedipac D.


advantages
In the main, the Sedipac 3D’s efficiency can be explained by:
- grit removal carried out at a maximum velocity of 40 m · h–1;
- an original and high performance grease remover due to its mix reactor and to its grease separation zone, characterised by a maximum reduction in upstream and downstream turbulence and by an induced surface current that propels, without creating any disturbance, floating matter towards the rotating collection scoop;
- a tried and tested lamellar settling tank (see lamellar settling tanks)
- easily installed due to its rectangular shape and to the absence of any connecting channels between the grit removal, grease removal and sedimentation zones;
- odour control made easy because a close cover can be fitted over the entire structure.
lamellar settling tanks with flocculation: the sedipac FD
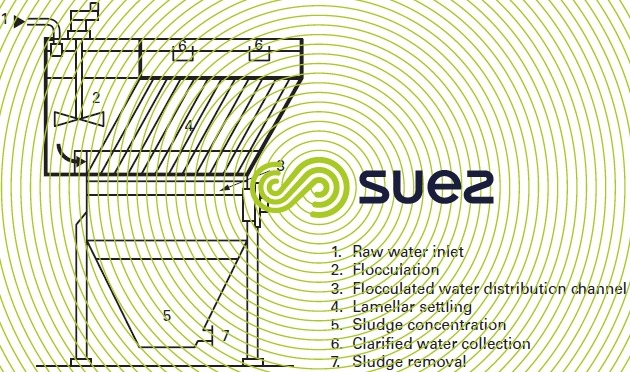
The Sedipac FD (figure 11) is a combined unit that houses a Coagulation-Flocculation zone and a Lamellar settling zone in the same enclosure. The settling zone may or may not be scraped depending on flow rate. The Sedipac FD is particularly well suited to compact UCD systems (see small standard units) and ideal for basic treatment plants. It may also be selected for plants having a higher flow rate (up to 450 m3 · h–1), especially in water that is sometimes loaded.


Bookmark tool
Click on the bookmark tool, highlight the last read paragraph to continue your reading later
















