recycling
Reading time:recycling rinse water through ion exchangers
This method can be used to recycle water after cations and anions are removed via ion exchange, with the exception of water that has to be sent for detoxification because it contains cyanides and/or high levels of grease or hydrocarbons.
Figure 62 covers the main closed system options.
Exchangers can be installed in a fixed position, with in situ regeneration, a technique that is viable for larger plants; alternately exchangers can be “mobile” and sent to an approved center for regeneration. This approach is most applicable for small plants (maximum volume of resin = 200 L) and requires constant availability of a spare set of regenerated exchangers.

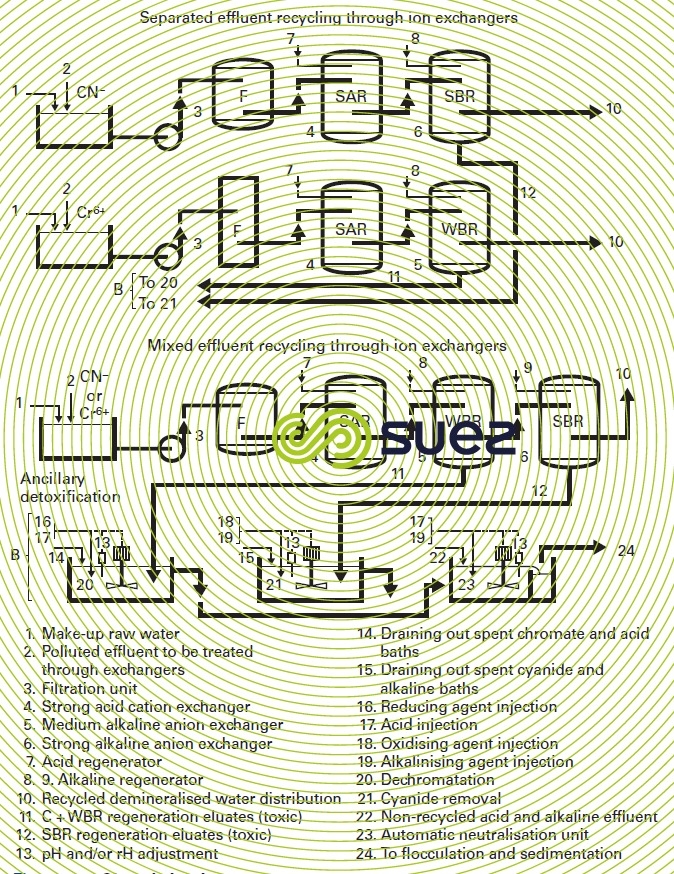

Regardless of the layout used, recycling plays two roles: water recovery (reuse) and contaminant concentration. Therefore, it needs to be systematically supplemented with a detoxification treatment.
The advantages of recycling using ion exchange are as follows:
- significant reduction in water consumption;
- production of extremely pure water, at low cost, with improved rinsing quality;
- pollution concentration (reduction in final treatment capacity);
- recovery of some costly products (gold, silver, chromate);
- chrome plating bath stabilisation.
The recovery of noble metals or those that are extremely toxic, can also be undertaken by continuous electrolysis in a "dead" rinsing bath. This technique applies more specifically to gold, silver, cadmium, copper and nickel.
degreasing bath maintenance
These baths become rapidly polluted by oil removed from the surface of treated components. Beyond a few % concentration of oil and grease, the degreasing quality becomes unacceptable and the bath has to be renewed.
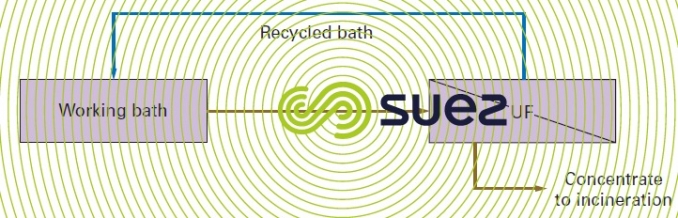
Ultrafiltration can be used to recover these free oils and thus extend the bath’s service life, achieving savings on chemical products.
This technique is used, for example, in steel mills (major consumer of degreasing agents) in cold rolling, on degreasing baths before continuous annealing, or before metal coating baths.
It is also used in the automotive industry.
When this type of system is used (figure 63), the service life of the baths can be tripled.


Bookmark tool
Click on the bookmark tool, highlight the last read paragraph to continue your reading later












